Personal finance is an essential life skill, yet it is often misunderstood or overlooked. Whether you’re a college student starting out, a new professional, or someone looking to take control of your money, understanding personal finance sets the foundation for long-term financial stability and security. This complete guide breaks down the fundamentals, strategies, and practical tips you need to navigate your financial journey confidently.
Understanding Personal Finance
The Meaning of Personal Finance
Personal finance refers to the management of an individual’s money, including earning, saving, investing, and spending. It encompasses all the decisions and strategies you employ to achieve financial security, meet short-term needs, and plan for future goals. Unlike business or corporate finance, personal finance is about optimizing your resources—salary, savings, assets, and investments—for a meaningful and secure life.
Why Is Personal Finance Important?
-
Financial Security: It helps you handle emergencies, avoid debt traps, and build a safety net.
-
Goal Achievement: Efficient financial planning allows you to save for education, travel, home buying, or retirement.
-
Peace of Mind: Knowing your finances are in order reduces stress and encourages confident decision-making.
-
Wealth Creation: Learning to grow your money through investments builds long-term wealth.
The Pillars of Personal Finance
Mastering personal finance involves understanding its five core pillars. Each contributes to a holistic financial strategy:
-
Income
-
Saving
-
Spending/Budgeting
-
Investing
-
Protecting (Insurance & Risk Management)
Let’s break down each pillar.
1. Managing Your Income
Your income is your most powerful financial tool. This includes your salary, business income, rental earnings, dividends, and any form of cash flow.
How to Optimize Income:
-
Pursue growth through upskilling or side hustles.
-
Understand your salary structure, tax implications, and benefits.
-
Track all income sources for proper budgeting.
2. Saving Money
Savings are the cornerstone of personal finance. They act as a buffer against unexpected events and form the foundation for future investments.
Types of Savings:
-
Emergency Fund: Reserve enough to cover 3-6 months of living expenses.
-
Short-Term Savings: For holidays, gadgets, or planned purchases.
-
Long-Term Savings: For retirement, children’s education, or buying a home.
Tips to Save Effectively:
-
Automate transfers to your savings account.
-
Avoid dipping into savings for daily expenses.
-
Compare interest rates and choose high-yield savings accounts.
3. Spending Wisely & Budgeting
Budgeting is about making conscious choices with your money. It ensures your spending aligns with your priorities and prevents overspending.
Popular Budgeting Methods:
-
50/30/20 Rule: Allocate 50% to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings.
-
Zero-based Budgeting: Every rupee/dollar is allocated a purpose.
-
Envelope System: Use physical or digital ‘envelopes’ for categories like groceries, entertainment, etc.
How to Create a Budget:
-
Track all your expenses for 1-2 months.
-
Categorize your spending.
-
Set reasonable limits and revise monthly.
Tips to Reduce Expenses:
-
Shop with a list and avoid impulse purchases.
-
Compare providers for bills (energy, mobile, Internet).
-
Use cashback and loyalty programs.
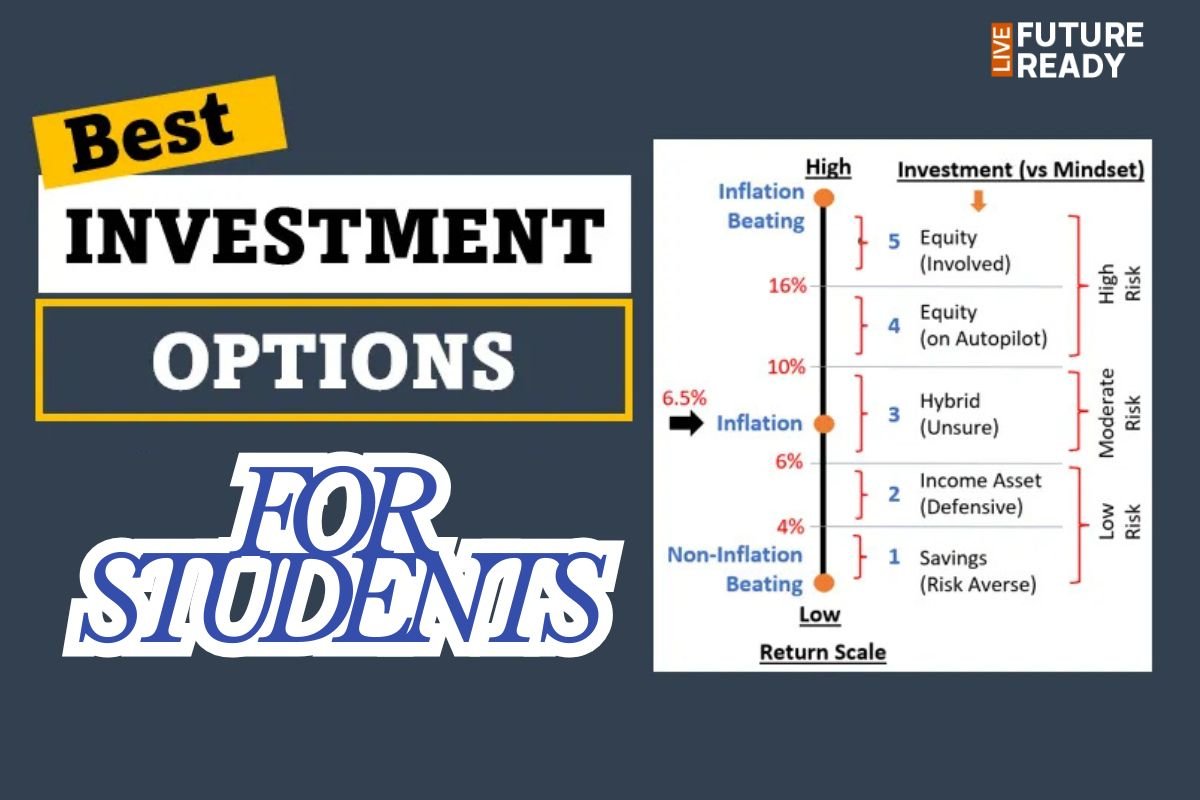
4. Investment Basics
Investing helps grow your wealth faster than regular saving. It harnesses compounding and market opportunities to meet bigger goals.
Types of Investments:
-
Stocks & Mutual Funds: Ownership in companies; high potential returns, riskier than savings.
-
Bonds: Loans to governments or companies; generally safer.
-
Real Estate: Property is a long-term investment with capital appreciation.
-
Gold: Often considered a safe haven.
-
Fixed Deposits/Certificates of Deposit: Provide steady, low-risk returns.
How to Start Investing:
-
Decide your risk tolerance and investment goals.
-
Learn the basics of various investment options.
-
Start with small amounts; use direct stock purchase plans or mutual funds.
-
Diversify your investments to spread risk.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
-
Chasing high returns without understanding risks.
-
Timing the market instead of regular, sustained investing.
-
Failing to review your portfolio periodically.
5. Protecting Your Finances: Insurance & Risk Management
Insuring your life, health, property, and income is crucial to safeguard your financial progress against unforeseen events.
Types of Insurance:
-
Health Insurance: Covers medical emergencies.
-
Life Insurance: Ensures your family’s security if you are absent.
-
Disability Insurance: Provides income if you are unable to work.
-
Property/Vehicle Insurance: Protects against loss or damage.
Risk Management Tips:
-
Choose appropriate coverage amounts.
-
Review insurance policies annually.
-
Ensure beneficiaries are updated.
Building a Strong Financial Foundation
1. Set Clear Financial Goals
Goals give your financial strategy direction—short-term (vacation, gadgets), medium-term (buying a car), and long-term (retirement, children’s college fund).
SMART Financial Goals:
-
Specific: Clearly define the goal (e.g., “Save ₹1,00,000 for a vacation”).
-
Measurable: Track progress.
-
Achievable: Be realistic; stretch but doable.
-
Relevant: Align with your life situation.
-
Time-bound: Set a deadline.
2. Develop Good Money Habits
Money habits build over time and influence your financial health. Consistency is key.
Essential Money Habits:
-
Record expenses and review monthly.
-
Save and invest before spending.
-
Avoid unnecessary debt; pay off credit cards in full.
-
Regularly educate yourself about financial products and news.
3. Avoid Common Personal Finance Mistakes
-
Not having an emergency fund.
-
Spending beyond one’s means.
-
Ignoring retirement planning.
-
Falling for “get-rich-quick” schemes.
-
Not seeking professional help when needed (financial advisors, accountants).
The Role of Credit in Personal Finance
Credit is a double-edged sword. Used wisely, it boosts convenience and can help you achieve goals; mismanaged, it leads to debt.
Credit Cards and Loans
Pros:
-
Convenient payments and purchases.
-
Builds credit score for future borrowing.
-
Rewards and cashback.
Cons:
-
High-interest rates on outstanding balances.
-
Late fees and penalties.
-
Over-borrowing risks.
Tips for Using Credit Responsibly:
-
Pay off credit card bills monthly.
-
Borrow only what you can repay.
-
Shop for low-interest loans and favorable terms.
Understanding Your Credit Score
A credit score measures your reliability as a borrower. It affects loan approvals and interest rates.
-
What matters: Payment history, utilization ratio, length of credit history.
-
How to improve: Pay bills on time, maintain a healthy mix of credit, avoid unnecessary borrowing.
Personal Finance Tools and Technology
In today’s digital age, a variety of tools help automate and simplify your financial life.
Budgeting Apps
-
Popular Apps: Mint, YNAB (You Need A Budget), GoodBudget, Walnut (India).
-
Features: Expense tracking, goal setting, alerts for bill payments.
Online Investment Platforms
-
User-friendly investment portals make stock, fund, and bond investing easy.
-
Robo-advisors offer personalized portfolios based on your risk tolerance and goals.
Digital Payments and E-wallets
-
Tools like Paytm, Google Pay, and Apple Pay facilitate cashless transactions and financial tracking.
Creating Your Personal Financial Plan
Developing a financial plan provides clarity and direction. It need not be complex but should cover all pillars of personal finance.
Steps to Create Your Financial Plan
-
Assess Your Current Situation: Net worth, income, expenses, liabilities.
-
Set Goals: Short, medium, and long-term.
-
Budget: Implement a budgeting plan.
-
Save and Invest: Automate savings and start with basic investment products.
-
Protect: Get essential insurance coverage.
-
Review and Adjust: Twice a year, review your progress and adjust as needed.
Overcoming Financial Challenges
Life is unpredictable. Unemployment, health issues, market downturns—these can disrupt plans. Building resilience requires proactive strategies:
-
Maintain a substantial emergency fund.
-
Prioritize essential expenses during tough times.
-
Reassess and cut non-essential costs immediately.
-
Seek income opportunities: freelancing, selling unused items, remote work.
Navigating Personal Finance at Different Life Stages
Young Adults
-
Begin with budgeting, saving, and understanding taxes.
-
Avoid lifestyle inflation as income grows.
-
Start investing with accessible products (SIPs, mutual funds).
Families
-
Plan for children’s education and family health insurance.
-
Adjust budgets for changing needs.
-
Align investments to family goals.
Mid-Career Professionals
-
Maximize retirement savings.
-
Diversify investments for growth.
-
Update insurances as required.
Pre-Retirement & Retirement
-
Consolidate and safeguard investments.
-
Focus on stable income sources.
-
Revise budgets to match fixed incomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How much should I save every month?
Aim to save at least 20% of your income. Adjust according to your goals and financial obligations.
Q2: What is the best investment for beginners?
Mutual funds, index funds, and high-yield savings accounts are beginner-friendly.
Q3: How do I start building credit?
Get a credit card, use it for small purchases, and pay the bill on time every month.
Q4: When should I get insurance?
Start early—health and life insurance are essential as soon as you are financially independent.
Q5: How do I improve my financial literacy?
Read reputable books, blogs, follow finance experts, and use online courses to stay updated.
Useful Resources for Beginners
-
Books: “The Psychology of Money” by Morgan Housel, “Rich Dad Poor Dad” by Robert Kiyosaki.
-
Websites: Investopedia, Moneycontrol, NerdWallet.
-
Courses: Local workshops, online courses on Udemy or Coursera.
Final Thoughts: Your Journey to Financial Freedom
Personal finance is not just about numbers—it’s about choices, discipline, and aspirations. By understanding the basics, setting clear goals, and developing sound habits, you empower yourself to thrive financially.
Remember, no matter where you start, everyone can achieve financial security with patience and perseverance. Use this guide as your roadmap to financial independence, and take that first step today.
Read more on our website: Future Ready, your go-to platform for the best educational content and latest updates.
Read More Related Blogs :-